DATA SCIENCE SYLLABUS for years 2022-2023
To start the learning journey in Data science you must first know the data science syllabus thoroughly. It will not only help you to make your curriculum easier to understand but also give a road map for your thrilled learning experience. Be it Statistics and mathematics, or SQL, or Python programming, we will be going deep down the course contents and give you a complete overview of the latest data science syllabus 2022-23.
There are different courses available for Data science with various levels of understanding and application techniques, but the core subjects remain big data, Business intelligence and Machine learning. Anexas has designed a course based on these subjects, industry requirements and individual requirements
If you want to start your career in data science, enroll in any of the following courses according to your requirements and learn data science with the latest syllabus
Data Science – Basic Course
Data Science – Intermediate Course
Data Science – Advance Course
This article consists of information on Data Science topics, concepts used in it and the latest syllabus of Data Science for years 2022-2023.

What is data science?
Data science is a field of study in which data is assessed based on business requirements and goals, and decisions are made depending on the patterns and results of the research analysis done by data scientists. This is achieved by deep diving into the data ocean and gaining the required knowledge through scientific techniques and processes. A data scientist is a person who writes algorithms for data analysis using a combination of concepts from maths, statistics, computer sciences, and business intelligence. Data science is present all around the world and is utilised in a wide range of domains like-
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing industries
- IT
- E-commerce
- Sales
- Telecommunication
- Finance
If you are equipped with a data science skill set, you will have a chance to strengthen your profession and add to the development of your organisation.
What are the subjects of data science?
The main subjects to focus on data science syllabus are
- Statistics – Data scientists are required to make decisions based on data available or mining the required data. Statistics is all about data and its interpretation.
- Programming Python- Programming skills are the major competencies for the data scientists; they code the required data structures and solve complex data architecture problems faced by the organisations.
- SQL – SQLis a data mining software which makes it easy to pull out data from the ocean of data present in the database.
- Machine learning – modern technology works on machine learning and Artificial intelligence, data scientists use these technologies for their research.
- Data interpretation skills – The data interpretation skills is one of the most important skills required to become a data scientist.
- Big data – Storing and managing huge amounts of data is becoming a major challenge in the modern world, big data deals with the ocean of data and its management.
- PowerBI – PowerBI is about data representation and visualisation. After researching and finding out the solution or decision, it is important to present the data in front of key stakeholders.
- Business communication – Business communication deals with understanding of data sharing and communication with business owners. Understanding of business decorum and organisational leadership is important.
- Decision making – Given the data is pulled out and statistical analysis is done, it is the decision-making skill which takes understanding of business for the data scientist to arrive at a decision.
Which are different courses in data science?
There are different courses one can pursue to become a data scientist. After completing class 12th, you can take diploma courses as well as graduation courses in data science. After graduation if you are interested in pursuing data science there are post graduate programmes are also available proceeding to masters and then PhD in data science. There is huge demand for data science professionals in various industries.
- Diploma in data science
- Certification course in data science
- Graduation course in data science for science students.
- Graduation courses in data science for business students.
- Post-Graduation in data science.
- PhD in data science.
The syllabus of data science?
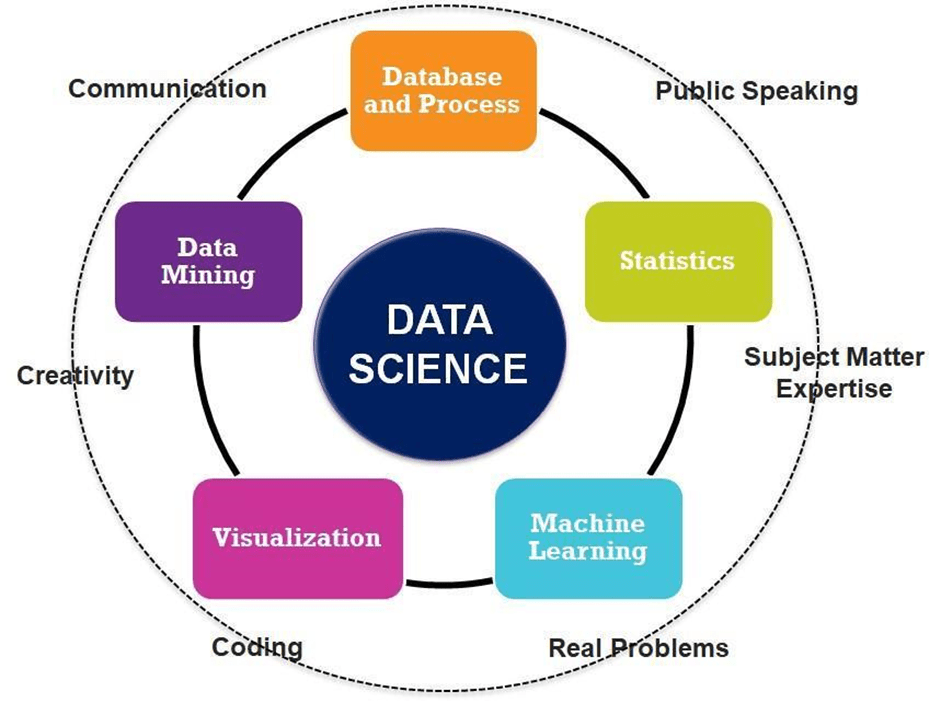
The syllabus of data science comprises computer science, data mining, machine learning, database and process, statistics, communication skills, data visualisation. These are one of the most important topics which you should focus on in the syllabus of data science year 2022-23. The focus and depth of study is based on your academic level i.e., diploma, undergraduate, graduation, post-graduation, PhD, or professional certification.
| Courses Offered by Anexas Europe Our upcoming Data Science course schedule | |||
| S. No. | Course Name | Dates | Time |
| 1. | Basic Data Science | ||
| 2. | Intermediate Data Science | ||
| 3. | Advanced Data Science | ||
| 4. | DATA SCIENCE (Full course) |
The syllabus of data science keeps on revising, but Anexas is well updated its course curriculum as per latest data science syllabus 2022-23
Data science syllabus in diploma?
Following are the topics covered in the basic diploma course in data science.
It is a 2year course containing 4 semesters consisting of all the basic data science topics to be taught at beginner level. The topics are:
- Introduction to Data Science
- Data Mining
- Cloud Computing
- Data Analysis
- Data Visualisation
- Data Model Selection and Evaluation
- Machine Learning
- Business Intelligence
- Data Warehousing
- Data Dashboards and Storytelling
Data science syllabus for graduation?
Data Science syllabus for BSc
BSc Data Science duration is 3 years. B.Sc. The Data Science Syllabus is divided into 6 semesters. The syllabus for each semester is different and includes Artificial Intelligence, Applied Statistics, Cloud Computing, along with elective subjects. The table below summarizes the BSc Data Science Syllabus semester-wise.
The topics which are covered in graduation are
- Mathematical & Statistical Skills
- Machine Learning
- Coding
- Algorithms used in Machine Learning
- Statistical Foundations for Data Science
- Data Structures & Algorithms
- Scientific Computing
- Optimization Techniques
- Data Visualisation
- Matrix Computations
- Scholastic Models
- Experimentation, Evaluation and Project Deployment Tools
- Predictive Analytics and Segmentation using Clustering
- Applied Mathematics and Informatics
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Business Acumen & Artificial Intelligence
Following table is showing semester wise subject in 6 semester courses:
| Semester I | Semester II |
| Linear Algebra | Probability and Inferential Statistics |
| Basic Statistics | Discrete Mathematics |
| Programming in C | Data Structures and Program Design in C |
| Communication Skills in English | Computer Organisation and Architecture |
| Programming in C Lab | Data Warehousing and Multidimensional Modelling |
| Microsoft Excel Lab | Data Structure Lab |
| – | Programming in R Lab |
| Semester III | Semester IV |
| Object-Oriented Programming in Java | Machine Learning, I |
| Database Management Systems | Cloud Computing |
| Operating Systems | Data Warehousing and Multidimensional Modelling |
| Design and Analysis of Algorithms | Operations Research and Optimization Techniques |
| Database Management Systems Lab | Time Series Analysis |
| Object-Oriented Programming in Java Lab | Machine Learning, I Lab |
| – | Data Warehousing and Multidimensional Modelling Lab |
| Semester V | Semester VI |
| Machine Learning II | Elective I |
| Introduction to Artificial Intelligence | Elective II |
| Big Data Analytics | Grand Viva |
| Data Visualisations | Major Project |
| Programming in Python Lab | |
| Big Data Lab | |
| Minor Project |
Data science syllabus for post-graduation?
Data Science syllabus for M.Sc.
MSc Data Science is a 2-year research-based postgraduate level program. The course revolves around Calculus, Descriptive Statistics, and C Programming, and the use of various technologies such as ML, DL, Python, and Spark are taught thoroughly.
| Semester I | Semester II |
| Mathematics for Spatial Sciences | Spatial Big Data and Storage Analytics |
| Applied Statistics | Data Mining and Algorithms |
| Fundamentals of Data Science | Machine learning |
| Python Programming | Advanced Python Programming for Spatial Analytics |
| Introduction to Geospatial Technology | Image Analytics |
| Programming for Spatial Sciences | Spatial Data Base Management |
| Business Communication | Flexi-Credit Course |
| Cyber Security | – |
| Integrated Disaster Management | – |
| Semester III | Semester IV |
| Spatial Modelling | Industry Project |
| Summer Project | Research Work |
| Web Analytics | – |
| Artificial Intelligence | – |
| Flexi-Credit Course | – |
| Predictive Analytics and Development | – |
MSc Data Science Electives
| Deep Learning | System Dynamics Simulation |
| IOT Spatial Analytics | Spatial User Interface Design and Implementation |
| Research Modelling and Implementation | Genomics |
| Exploratory Data Analysis | Multivariate Analysis |
| Stochastic Process | Programming for Data Science in R |
| Hadoop | Image and Video Analytics |
| Internet of Things | Identification and Data Collection |
Data science syllabus for a M. Tech in data science?
MTech in Data Science is a 2-year research-based postgraduate level program. The course revolves around Calculus, Descriptive Statistics, and C Programming, and the use of various technologies such as ML, DL, Python, and Spark are taught thoroughly.
Following is semester wise subjects to be covered during the course
| Semester I | Semester II |
| Data Science Programming | Data Analytics and Graphs |
| Data Mining and Warehousing | Empirical Research |
| Econometrics | Advanced-Data Analytics |
| Construction Economy and Finance | Big Data |
| Data Analytics Mathematics | Open Elective II |
| Open Elective I | Project |
| Laboratory | Laboratory |
| Semester III | Semester IV |
| Open Elective III | Evaluation of project and Viva |
| Project | Seminar |
| Open Elective IV | Training and Internship |
| Project | – |
MTech Data Science Electives
| Deep Learning | Natural Language Processing |
| Artificial and Computational Intelligence | Stream Processing and Analytics |
| Data Visualisation and Interpretation | Graphs-Algorithms & Mining |
| Optimization Methods for Analytics | Big Data Systems |
| Advanced Topics in Data Processing | Information Retrieval |
| Probabilistic Graphical Models | Data Warehousing |
| Systems for Data Analytics | Ethics for Data Science |
Data science syllabus for certification courses?
Professional certification courses are also available for data science where all the topics of data science are covered. Anexas is pioneer in training data science professionals the details are given below
Data Science courses with Anexas
If you are new to Data Science, Anexas is the right place to start. Learn about Data Science and all its components and become a Data Scientist. Gain knowledge from skilled industry experts who have more than 15 years of experience in the corporate market and have worked with the biggest organisations in the world. Get valuable certificates in your name and become a Data Scientist. Datamitum in collaboration with Anexas brings you a Data Science course where you can invest your time, money, and effort in the right direction
How will the Data Science course benefit you?
- Learn to use various industry-level tools
- Learn different disciplines of Data Science
- Inculcate Leadership skills
- Get international career opportunities
- Gain advanced skill sets
- Get better job profiles
- Expand your Influential network
- Apply knowledge of AI, ML, Python and NLP at your workplace
- Learn the use of Probability and other statistical tools in projects
- Get insights of Deep Learning
Why to Choose Anexas?
With Anexas we are providing world class training, taking into consideration the ongoing demand of data science in top industries. Following are the key features of our courses:
- 135 hours of interactive online live training with industry experts
- Content-rich study material
- Free eBooks
- Projects for better understanding
- Assignments for each module
- Participants will be certified by ANEXAS Europe
- International recognition
- Tools required for the training
- Open-book online test for certification after each module
- 100% Pass rate guaranteed
- Lifetime membership to Anexas Alumni group
- Mock Interviews for job preparations
- Guidance for resume-building
- Get a chance to win cashback benefits
- Online Line Customer support 24*7
Syllabus of data science courses with Anexas
Anexas offers a comprehensive course for future ready professionals. The Course is divided into three levels i.e., Basic, Intermediate, and advanced.
The details of all the subjects are listed below: .
Data Science course: Basic Level
The basic level course content has all the important topics that are required for students who are starting the data science course and want to learn from basics.
| Level 1 – Basic | ||
| Delivery | Topics | Delivery Mode |
| Python | Installation – Anaconda, PyCharm, Virtual environment | Live Code – Jupyter/Colab/PyCharm + Slides |
| Introduction to python | ||
| Basic Syntax, comments, Variables | ||
| Data Types, Numbers, Casting, Strings, Booleans | ||
| Operators, Lists, Tuples, Sets, Dictionaries | ||
| If…Else, While Loops, For Loops | ||
| Functions, Lambda, Arrays | ||
| Arrays, Classes/Objects, Inheritance, Iterators | ||
| Scope, Modules, Dates, Maths, JSON | ||
| PIP, Try…Except, User Input P, String Formatting | ||
| File Handling, Read Files, Write/Create Files, Delete Files | ||
| NumPy | ND array, Data types, Array Attributes, Indexing and Slicing | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides |
| Array manipulation, Binary operator, String Function | ||
| Arithmetic, Statistical, Matrix, linear algebra, sort, search, counting | ||
| Pandas | Data manipulation, Viewing, selection, grouping, merging, joining, concatenation | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides |
| Working with text data, visualisation, CSV, XLSX, SQL data pulling, operations | ||
| SciPy | Statistics, Linear algebra, models, special functions, optimization | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides |
| Probability & Stats Applications | ||
| Probability | Basic Probability, Random experiments, conditional Probability, Independent Events, | Mostly Live numerical solving + Slides + mathematical intuition + codes |
| Bayes theorem, Permutation, combination | ||
| Random variable, Discrete/Continuous RV, PDF, PMF, CDF | ||
| Joint Probability Distribution, Conversion techniques, EV, variance, SD | ||
| Covariance, Correlation, Chebyshev Inequality, Law of Large number | ||
| Central limit Theorem, Percent & Quantiles, Moments | ||
| Skewness & Kurtosis, Gaussian, Binomial, Standard Normal, Distribution | ||
| poison, Multinomial, Hypergeometric, Uniform, Exponential Distribution | ||
| Statistics | [Mean, median, mode] (Sample/population), Expected values, variance, standard deviation | Mostly Live numerical solving + Slides + mathematical intuition + codes |
| Sampling distribution, Frequency distribution, Estimation Theory | ||
| confidence interval, Maximum Likelihood Estimation | ||
| Hypothesis Testing – Chi Square, Student’s T, F Distribution, Z test | ||
| Hypothesis Testing – Type-I, Type- II, p Values, Relationship between NULL & Alternative | ||
| Least Square Methods – Numerical | ||
| Data Pre-Processing | Data Cleaning – Handling Missing Values (Data Imputation), Dealing with Noisy data (Binning Technique) | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides |
| Advance Data cleaning – Will be referred while Regression, clustering topics | ||
| Data Transformation Techniques- Normalisation (minmax, log transform, z-score transform etc.), Attribute Selection, Discretization, Concept Hierarchy Generation | ||
| Data Reduction: Data Cube Aggregation, Numerosity Reduction, Dimensionality Reduction | ||
| Data Visualisation | Data Mapping, Charts, Glyphs, Parallel Coordinates, Stacked Graphs | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides |
| Bar, Pie, Line Charts, bubbles, geo maps. Gauge, whisker charts, Heatmaps, scatterplots, plotting images, videos, motion charts, performing EDA | ||
| Building Dashboard – Live implementation – PowerBI | ||
| ML Algos | ||
| Linear Regression | Implementation of Numerical intuitions | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| Regression basics: Relationship between attributes using Covariance and Correlation | ||
| Relationship between multiple variables: Regression (Linear, Multivariate) in prediction. | ||
| Residual Analysis: Identifying significant features, feature reduction using AIC, multicollinearity | ||
| Multiple Linear Regression | Polynomial Regression | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| Regularisation methods | ||
| Lasso, Ridge and Elastic nets | ||
| Categorical Variables in Regression | ||
| Non-Linear Regression | Logit function and interpretation | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| Types of error measures (ROCR) | ||
| Logistic Regression in classification | ||
| Clustering | Distance measures – Euclidean distance | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| Different clustering methods (Distance, Density, Hierarchical) | ||
| Iterative distance-based clustering; | ||
| Dealing with continuous, categorical values in K-Means | ||
| Constructing a hierarchical cluster | ||
| K-nearest neighbours, K-Medoids, k-Mode and density-based clustering | ||
| BIRCH, DBSCAN, Mean Shift, Spectral Clustering, Gaussian Mixture Model | ||
| Association Rule mining | The applications of Association Rule Mining: Market Basket, Recommendation Engines, etc. | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| A mathematical model for association analysis; Large item sets; Association Rules | ||
| Apriori: Constructs large item sets with mini sup by iterations; Analysis discovered association rules; | ||
| Application examples; Association analysis vs. classification | ||
| FP-trees, PageRank |
Data Science course: Intermediate Level
Data science course at intermediate level contains deeper knowledge and topics about Database, NLU, and statistics.
| Level 2 – Intermediate | ||
| Delivery | Topics | Delivery Mode |
| Classification | Naïve Bayes Classifier: Model Assumptions, Probability estimation | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| Required data processing, M-estimates, Feature selection: Mutual information | ||
| Random Forest Algo + Implementation | ||
| classification using Logistics, K nearest Neighbours | ||
| Decision Trees: ID4, C4.5, CART | ||
| Support Vector Machines: Linear learning machines and Kernel space, Making Kernels and working in feature space | ||
| SVM for classification and regression problems. | ||
| Feature Engineering | Feature Reduction/Dimensionality reduction | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| Principal components analysis (Eigenvalues, Eigen vectors, Orthogonality) | ||
| Validation Techniques (Cross-Validations) | ||
| Ensembles methods | Bagging & boosting and its impact on bias and variance | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| C5.0 boosting | ||
| Gradient Boosting Machines and XGBoost | ||
| Database | Build Dataset from large database | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| SQL queries & Protocol Building | ||
| Creating Feature Store using SQL | ||
| in-Depth PostgreSQL | ||
| Introduction to Statistical NLP Techniques | Introduction to NLP | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| Pre-processing, NLP Tokenization, stop words, normalisation, stemming and lemmatization | ||
| Pre-processing in NLP Bag of words, TF-IDF as features | ||
| Language model probabilistic models, n-gram model and channel model | ||
| Hands on NLTK | ||
| Word2vec | ||
| Glove | ||
| POS Tagger | ||
| NER | ||
| POS with NLTK | ||
| Gensim | ||
| TF-IDF with NLTK | ||
| NLP- NLU Delivery | Introduction to sequential models | |
| Introduction to RNN | ||
| Intro to LSTM | ||
| LSTM backprop through time | ||
| Hands on keras LSTM | ||
| Sentiment Analysis | ||
| Sentence generation | ||
| Machine translation | ||
| Advanced LSTM structures | ||
| Keras- Machine Translation | ||
| Encoder decoder with attention | ||
| Encoder Decoder – Auto Encoder | ||
| Understanding transformers | ||
| Attention Models Intuitions | ||
| Introduction to BERT | ||
| GPT | ||
| Chatbot -hands-on |
Data Science course: Advanced Level
The advanced level in data science contains all the topics which will groom you to become an expert in data science which is required by top companies today.
| Level 3 – Advanced | ||
| Delivery | Topics | Delivery Mode |
| Neural Networks Using TensorFlow and Keras | Basic Mathematics – DL | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| Introduction to Perceptron & History of Neural networks | ||
| Activation functions a. Sigmoid b. Relu c. SoftMax d. Leaky Relu e. Tanh f. Exponential Linear Units (ELU) g. Swish |
||
| Gradient Descent | ||
| Learning Rate and tuning | ||
| Optimization functions | ||
| Introduction to TensorFlow | ||
| Introduction to keras, Theano, pytorch – hands-on | ||
| Back propagation and chain rule | ||
| Fully connected layer | ||
| Cross entropy | ||
| Weight Initialization | ||
| Regularisation | ||
| coding perceptron | ||
| Q&A | ||
| Computer Vision | ||
| Working with images & CNN Building Blocks | Working with Images Introduction | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| Working with Images – Digitization, Sampling, and Quantization | ||
| Working with images – Filtering – OpenCV | ||
| Hands-on Python Demo: Working with images | ||
| Introduction to Convolutions | ||
| 2D convolutions for Images | ||
| Convolution – Backward – hands-on | ||
| Transposed Convolution and Fully Connected Layer as a Convolution – hands-on | ||
| Pooling: Max Pooling and Other pooling options – practical | ||
| CNN Architectures and Transfer Learning | CNN Architectures and LeNet Case Study | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| Case Study: AlexNet | ||
| Case Study: ZFNet and VGGNet | ||
| Case Study: GoogleNet | ||
| Case Study: ResNet | ||
| GPU vs CPU | ||
| Transfer Learning Principles and Practice | ||
| Hands-on Keras Demo: SVHN Transfer learning from MNIST dataset | ||
| Transfer learning Visualisation (run package, occlusion experiment) | ||
| Hands-on demo -T-SNE | ||
| Hands -on CNN nets | ||
| Hands-On OCR, Face Recognition, Object Detection, Pose Estimation, 3D estimations | ||
| CNNs at Work – Semantic Segmentation | CNNs at Work – Semantic Segmentation | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| Semantic Segmentation process | ||
| U-Net Architecture for Semantic Segmentation | ||
| Hands-on demo – Semantic Segmentation using U-Net | ||
| Other variants of Convolutions | ||
| Inception and MobileNet models | ||
| Object Detection | CNNs at Work – Object Detection with region proposals | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| CNNs at Work – Object Detection with Yolo and SSD | ||
| CNNs at work- Siamese Network for Metric Learning | Siamese Network as metric learning | Live Code – Jupyter/colab/PyCharm + Slides + Real time Use cases coding |
| How to train a Neural Network in Siamese way | ||
| Hands-on demo – Siamese Network |
Conclusion:
“The world’s most valuable resource today is no longer gold or oil, but data.” In this digitally driven economy, Data is extremely valuable and the key to the smooth functioning of every organisation as it helps take quicker and better decisions. The Data Science domain is expected to see 250,000 new openings in 2022, an increase of 62% compared to 2021.There is a huge opportunity in the field of data science and Anexas is with you to make your industry ready with our course.
If you think this is too much information to take and how you are going to keep up with the changing syllabus, you don’t need to worry. Take this free introductory session on Data Science and learn how Anexas provides lifetime access to course content and recorder video when you join the course.
FAQs
Does data science Certification increase your salary?
Yes, Data science Certification will increase your salary. A survey conducted across companies showed that the Data science professionals get 40% hike in the salary
Is the Data science certification worth it?
Yes, Data science certification is worth it. Data science teaches you tools and techniques that will give you a huge advantage to develop your data analytics skills. It also opens many doors for your career opportunity.
Is it compulsory to have a bachelor’s degree to pursue data science?
No, Data science can be done after 12th by certification courses or diploma in data science.
Will Data science help my career?
Yes, Data science will help your career as it teaches you knowledge that can be applied in any projects irrespective of departments. Since Data science is recognized globally you can apply for companies all over the globe.
Which is better – Data analytics or Data science?
Data science is better than data analyst as it consists of all the knowledge data analysts have. So why Soldier when you can become a General.
Do I need to learn advanced level programming for data science?
No, Data science involves an intermediate level of programming skills
Also read: Business Analytics vs Data Science