Table of Contents
Determining Process Sigma in Lean Six Sigma
- 28916 views
Determining process sigma is a very commonly used metric for evaluating the performance of a process. Process sigma can be calculated for
- Continuous data
- Defect data
- Defective data
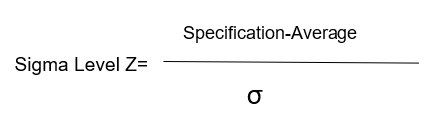
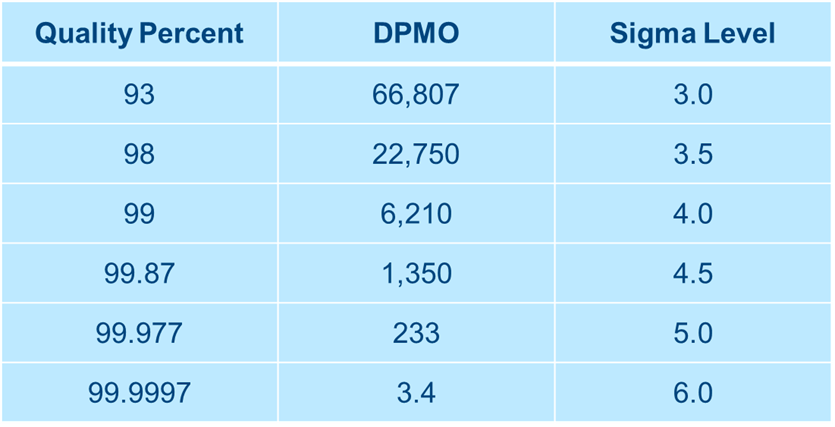
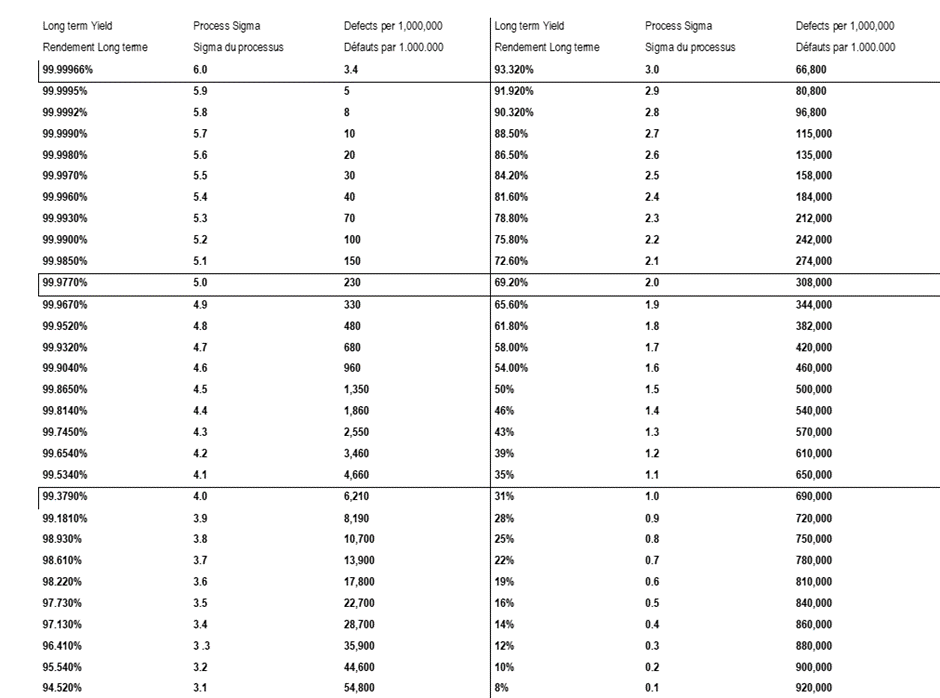
Sigma level corresponds to a certain defect per million opportunities (DPMO). The higher the sigma level (Z), the lower the DPMO which means a lower defect rate.
Companies are continuously seeking tools that can streamline their processes and elevate their efficiency. One such groundbreaking tool is the process sigma calculator. This sigma level calculator doesn’t just quantify process performance; it transforms raw data into actionable insights. By pinpointing variations and inefficiencies through sigma values, businesses can achieve a higher standard of quality and productivity.
Calculating Sigma level is an important measurement method that we use in Lean Six Sigma projects. This article will cover all the tips and tricks which will help in successfully determining process sigma for your process and clearing the Lean six sigma certification exam.

Why Use Six Sigma as a Metric?
Calculating Process sigma is a more sensitive indicator than the quality percentage.
Types of data and the examples
Below are the listed steps to calculate the process sigma for continuous data and attribute data. Follow the tips given below and note down the formulae and practice them at least twice to master determine process sigma. Given below are proven and tested tips by industry experts-
There are two types of data- Continuous or Variable and Attribute or Categorical.
Continuous data: Continuous data is data that can take any numerical value. Weight, height, temperature and length are all examples of continuous data. Some continuous data will change over time; the height of a baby in its first year or the temperature in a hall throughout the day.
Attribute data: Attribute (category) data is labelled. It is measured on nominal or ordinal scales.
| Continuous Data Examples | Attribute Data Examples |
| Time taken to process a purchase order | Number of bugs in program |
| Turn around Time for issuing invoice | Number of protocol violation during call |
| Average response time to customer orders | Number of printing defects on a shipping label |
| Accounts receivable | Number of typo error per sales contract |
| Amount of time it takes to close it | Number of new hires per 100 applicants |
How to determine the process sigma for Continuous or variable data?
- Find Specification of the product or service which needs to be measured process sigma
- Lower Specification Limit
- Upper Specification Limit
- Collect a minimum of 30 sample sizes.
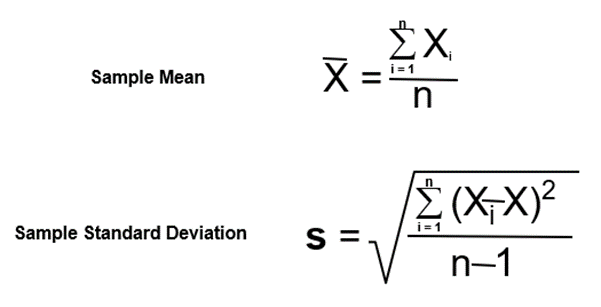
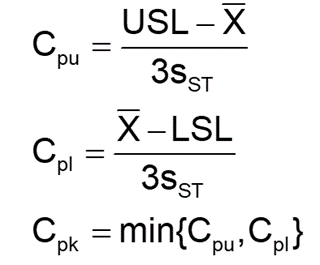
- Calculate Sample mean and standard deviation using the following formula or use an excel sheet or Minitab software.
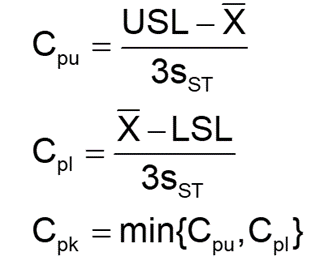
- Then substitute the values in the following formula. Calculate process capability index, Cpk = min{Cpu, Cpl} where Cpu and Cpl are calculated for the upper limit and lower limit, respectively
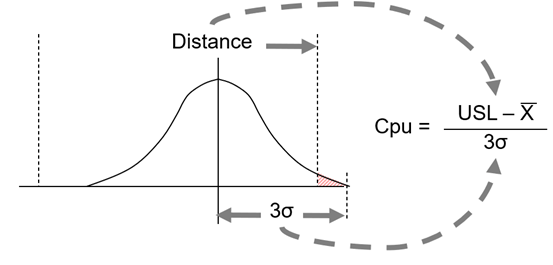
- Sigma performance level = 3*Cpk
- Sigma short-term performance level = Z-score + 1.5
- Even if dealing with discrete variables, we use the Z-score that corresponds with the yield
- This gives us the capability if there were no shift
- Add 1.5 to the Z-score as a “standard amount of shift”
- Sigma performance level is an all-inclusive process/product performance indicator figure
- Includes capability and shift
How to determine the process sigma for Attribute or Categorical data?
- Unit: the item produced or processed
- Defect: any event that does not meet the specification of a CTQ as defined by the customer
- Defect opportunity: any event which can be measured that provides a chance of not meeting a customer requirement (specification)

- Calculate the number of Defects Per Million Opportunities

- In the Sigma table, look at the Sigma value relating to the DPMO determined
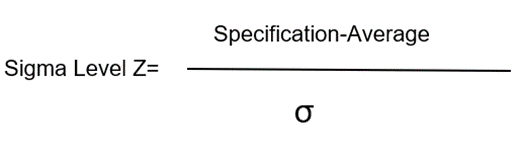
Some formulae to keep in mind

Determining Process Sigma – Example exercise 1
Find the sigma level (Z) for pizza outlet? Average delivery time is 30minutes, Standard deviation is 5minutes, Upper specification limit is 60minutes
Determining Process Sigma – Example exercise 2
Higher the sigma level (Z), lower is the DPMO which means _____ defect rate
Determining Process Sigma – Example exercise 3
Using Six Sigma methodology, a process at 4 sigma would have a failure rate of ____
Answers for skills-building exercises
- The answer for the first sample exercise is 6
- The answer for the second sample exercise is: lower.
- The answer for the third sample exercise is: 6210 ppm
Conclusion
In conclusion when you calculate the Sigma Level, you occasionally need to distinguish between Short-Term and Long-Term. Short-Term data is data that is gathered for a short period when typically only common causes are present. Long-Term data is data that is collected for a long period when both common and special causes are present. Determining process sigma is a measure of variation in a process relative to customer specification expressed as a number of standard deviations on a normal distribution.
Also Read: Brainstorming Techniques for Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
- Aligned with IASSC, CSSC, ASQ
- 50+ projects + 2 live projects
Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
- Aligned with IASSC, CSSC, ASQ
- 50+ projects + 2 live projects
Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt
- Aligned with IASSC, CSSC, ASQ
- 50+ projects + 2 live projects